Cimquest’s Additive Manufacturing 3D Printing Solutions
Cimquest’s line of 3D Printers includes systems for plastic and metal 3D printing. We realize there isn’t an “all-in-one” additive manufacturing system that can accomplish everything so we offer multiple technologies that serve a diverse set of applications and industries. From entry-level 3D printers to industrial systems, we have the tech to help you produce conceptual & functional prototypes, end-use parts, models, manufacturing tooling, jigs & fixtures, and more. We provide full-service implementation and our award-winning technical support team will give you piece of mind whenever an issue arises.
Our 3D Printing Solutions and Technologies
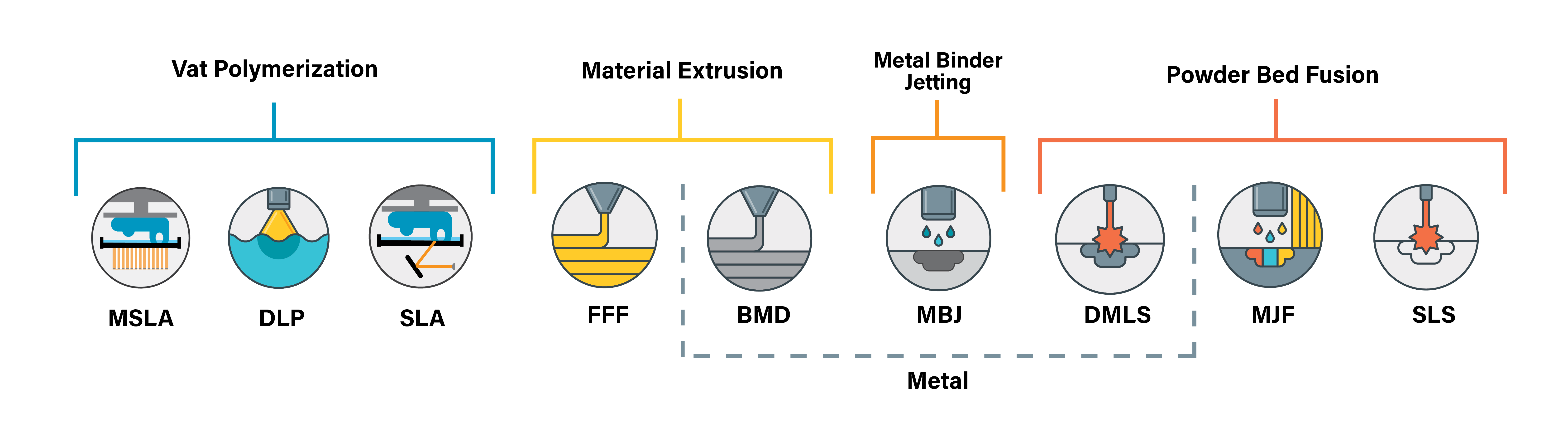
Vat Polymerization
Vat Polymerization, basically, turns solid under a proper wave light. Light sources, such as lasers, projectors, LCD panes, can be different, which defines the technology type.
Key Benefits:
- High Accuracy and Feature Detail
- Injection Mold quality surface finish
- Parts with exceptional accuracy, superior part properties, fine feature detail
Powder Bed Fusion
Powder Bed Fusion 3D printing is an additive manufacturing method that uses raw material in powder form.
Formlabs SLS Printer: Fuse 1+
selective laser sintering (SLS) 3D printers for professionals.
Key Benefits:
- Fine feature detailed prints
- Injection Mold quality surface finish
- Industrial capabilities at desktop price
Key Benefits:
- Low cost of entry without sacrificing high-quality results
- Small footprint, short adoption time & easy installation into any shop
- High density, weldable, & complex parts on demand
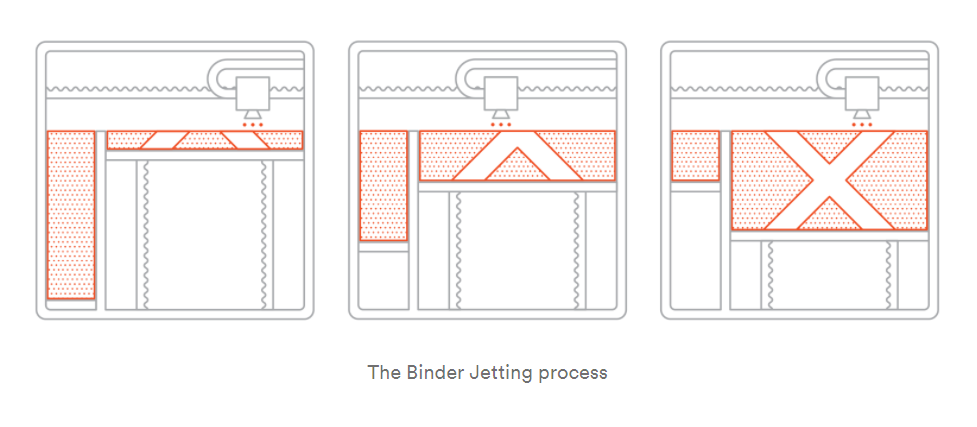
Metal Binder Jetting
Binder jetting is an additive manufacturing process in which an industrial printhead selectively deposits a liquid binding agent onto a thin layer of powder particles — foundry sand, ceramics, metal or composites — to build high-value and one-of-a-kind parts and tooling.
Key Benefits:
- The world’s first metal binder jetting system designed to bring metal 3D printing to machine shops
- Complex geometries not achieved through CNC
- Easy to use & operate
Bound Metal Deposition (BMD)
Bound Metal Deposition™ (BMD) is an extrusion-based metal additive manufacturing (AM) process where metal components are constructed by extrusion of a powder-filled thermoplastic media. Bound metal rods—metal powder held together by wax and polymer binder—are heated and extruded onto the build plate, shaping a part layer-by-layer. Once printed, the binder is removed via the debind process, and then sintered—causing the metal particles to densify.
Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF)
Material extrusion is a 3D printing process where a filament of solid thermoplastic material is pushed through a heated nozzle, melting it in the process. The printer deposits the material on a build platform along a predetermined path, where the filament cools and solidifies to form a solid object.
Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF)
A 3D printing process where a filament of solid thermoplastic material is pushed through a heated nozzle, melting it in the process. The printer deposits the material on a build platform along a predetermined path, where the filament cools and solidifies to form a solid object.Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF) Printers
 Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF)
Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF)
These are the most commonly available and the least expensive types of 3D printing technology. A spool of filament is loaded into the 3D printer and fed through to a printer nozzle in the extrusion head.
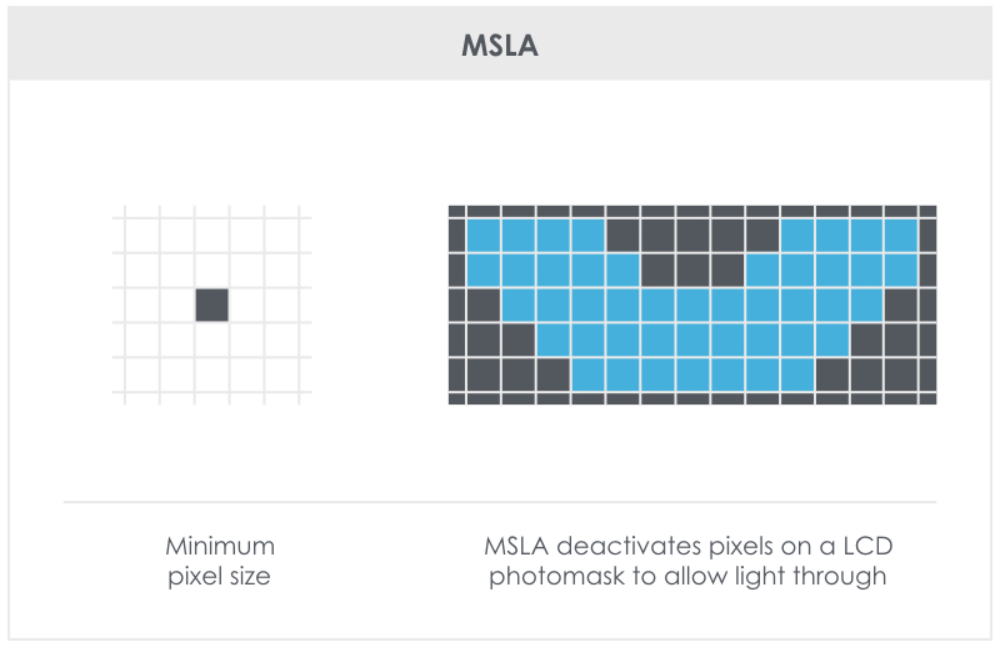
VAT Polymerization
A 3D printing process where a light source selectively cures a photopolymer resin in a vat. The two most common forms of Vat Polymerization are SLA (Stereolithography) and DLP (Digital Light Processing). The difference between these types of 3D printing technology is the light source they use to cure the resin. SLA printers use a point laser, in contrast to the voxel approach used by a DLP printer.VAT Polymerization Printers
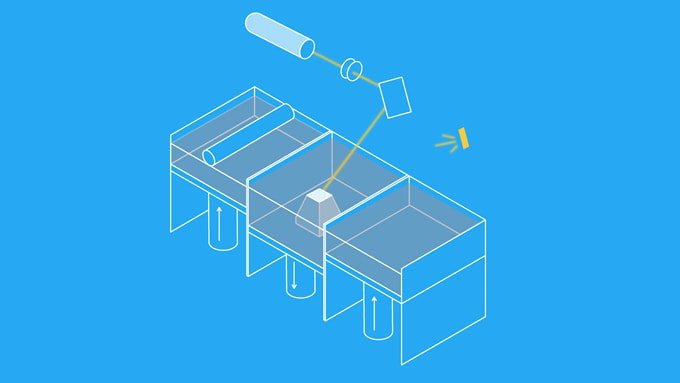
 Stereolithography (SLA)
Stereolithography (SLA)
SLA printers use mirrors with one positioned on the X-axis and another on the Y-axis which rapidly aim a laser beam across a vat of resin, selectively curing and solidifying a cross-section of the object inside this building area, building it up layer by layer.

DLP is a 3D printing (additive manufacturing) technology which utilizes light and a liquid resin to make solid parts and products.
Multi Jet Fusion
A 3D printing process where a thermal energy source will selectively induce fusion between powder particles inside a build area to create a solid object. Many Powder Bed Fusion devices also employ a mechanism for applying and smoothing powder simultaneous to an object being fabricated so that the final item is encased and supported in unused powder.Multi Jet Fusion Printers
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
This process creates an object with Powder Bed Fusion technology and polymer powder.
Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS)
Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) produce objects in a similar fashion to SLS. The main difference is that these types of 3D printing technology are applied to the production of metal parts.
Metal Binder Jetting
A 3D printing process where a liquid bonding agent selectively binds regions of a powder bed. It’s similar to SLS, with the requirement for an initial layer of powder on the build platform, but unlike SLS, which uses a laser to sinter powder, Binder Jetting moves a print head over the powder surface depositing binder droplets. These droplets bind the powder particles together to produce each layer of the object.Material Jetting Printers

Metal powder is bound using a polymer binding agent. Producing metal objects using Binder Jetting allows for the production of complex geometries well beyond the capabilities of conventional manufacturing techniques.