Introducing Formlabs BioMed Flex 80A Resin and BioMed Elastic 50A Resin
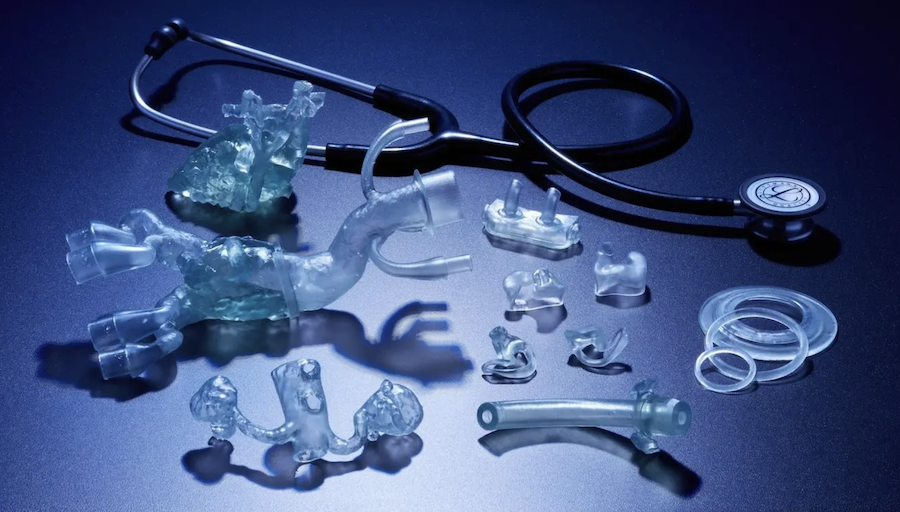
Formlabs is excited to introduce two novel materials designed for the direct 3D printing of elastomeric, biocompatible medical devices and models: BioMed Flex 80A Resin and BioMed Elastic 50A Resin. These new materials represent a significant expansion in medical application areas, particularly in the realm of anatomical modeling.
Traditionally, professionals looking to create soft anatomical models have grappled with the challenges of multi-step silicone molding processes, labor-intensive procedures resulting in limited geometries, messy outcomes, and excessive time and money spent. Alternatively, they have settled for costly contract manufacturing or rigid models.
Enter BioMed Flex 80A Resin and BioMed Elastic 50A Resin, which offer healthcare professionals the unprecedented ability to merge the advantages of traditional elastomeric and biocompatible materials with the user-friendly experience and streamlined workflows inherent to Formlabs resin 3D printers.
Why Use Soft Anatomical Models?
Soft anatomical models offer a great value to healthcare providers and patients alike. As cases become more complex, and interventions more unique, anatomical models can be used by healthcare providers to map pathology, plan interventions, gain a three-dimensional understanding of anatomical spatial relationships, pre-fit medical equipment, and practice approaches, all before the patient enters the operating room (OR).
Soft models in particular pose a great advantage to surgical training by providing medical residents, fellows, and students with the ability to cut directly into tissue-simulating material. Because BioMed Flex 80A Resin and BioMed Elastic 50A Resin are biocompatible and sterilizable, models can also be taken directly into the OR while surgery is underway to be used as an anatomical reference or sizing tool.
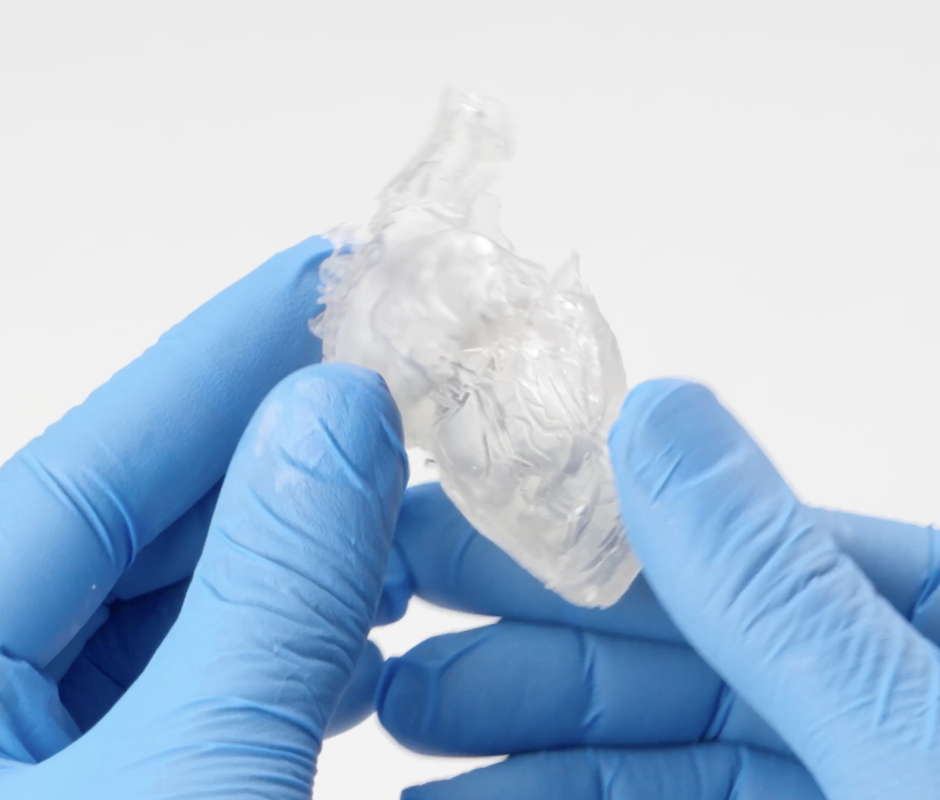
Anatomical model of a heart printed in BioMed Elastic 50A Resin.
The use of soft anatomical models offers advantages to patients as well. Not only are patient outcomes better when the physician has the opportunity to plan using a patient-specific model, but patient consent is enhanced when an anatomical model is used to inform them about the solution being offered. With an anatomical model, patients gain insights into the scale and scope of the issue as well as gain a more comprehensive understanding of what proposed treatments entail.






Leave A Comment