How Harlequin Design Uses SLA Printing to Meet Tight Deadlines
Harlequin Design, a leader in visual merchandising, utilizes SLA 3D printing to create high-quality, custom displays for luxury brands such as Hermès, Dior, and Louis Vuitton. This technology helps them meet tight deadlines and maintain their reputation for excellence. Here’s an in-depth look at their process: 1. Designing Props for Retail Theater Harlequin specializes in crafting unique, eye-catching displays that enhance the in-store shopping experience. These displays are often updated seasonally to align with the latest fashion trends, ensuring that each installation is fresh and relevant. 2. Transitioning to SLA Printing Initially, Harlequin used FDM printers but faced challenges with reliability and print quality. The switch to Formlabs’ SLA printers marked a significant improvement, providing the precision and consistency needed to produce intricate designs. 3. Enhancing Speed and Flexibility With a fleet of Form 3L printers, Harlequin can produce parts quickly and efficiently in-house. This capability reduces their reliance on external suppliers, cuts production costs, and allows for rapid iteration and prototyping. 4. Unlocking New Design Possibilities SLA printing technology enables Harlequin to create complex, detailed designs that were previously unattainable. This advancement has expanded their creative horizons, allowing for more innovative and precise displays. 5. Ensuring Rapid Delivery The ability to print [...]
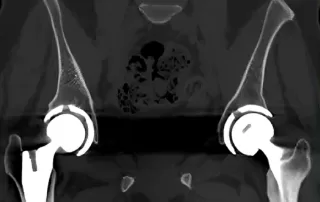
Innovative Implant Design: From Imaging to Surgical Application
Innovative Implant Design: From Imaging to Surgical Application Hip replacement is common for osteoarthritis, using off-the-shelf acetabulum cups. However, some patients need bespoke implants due to complex conditions like previous surgeries or extensive hip damage. Complex hip replacements pose surgical challenges due to scar tissue, distorted anatomy, fragile or dead bone, and tumors. Bespoke implants require unique bone preparation and precise fitting, often through small incisions and avoiding nerves and blood vessels. Accurate design and manufacturing of implants are critical, involving multiple steps from patient scans to surgery. Starting with accurate imaging The patient-specific hip implant must start with CT or MRI imaging to analyze bone quality and morphology, helping the team establish implant positioning. These images may be augmented with standing x-rays for a 3D understanding of pelvic orientation. The next step must convert 2D medical images into a 3D model using Simpleware. This software imports image data and uses manual and AI-driven segmentation to define anatomical structures, generating a 3D model for accurate measurements. The 3D model must then be exported to Geomagic Freeform, which is quick and easy. The resulting model can include labels and a bone density color map. From 3D modeling to printable design Freeform must produce manufacturable, [...]
Introducing HP 3D HR PA 12 FR Enabled by Evonik: A Revolutionary Flame-Retardant Material
We are excited to announce the launch of HP 3D HR PA 12 FR, a cutting-edge material developed in collaboration with Evonik. This innovative material is designed to meet the highest standards of safety and efficiency, making it an ideal choice for a wide range of applications. Key Features: Flame-Retardant: HP 3D HR PA 12 FR is a halogen-free material that targets the UL94 V0 flammability standard, ensuring superior fire resistance. High Powder Efficiency: With a 50% reusability ratio, this material maximizes powder efficiency, reducing waste and lowering costs. Premium Surface Aesthetics: Produce high-quality parts with excellent surface finishes, enhancing the overall appearance and functionality of your products. Applications: Industrial: Perfect for electrical components housing, covers, casings, cable holders, cable fasteners, battery holders, and more. Consumer Goods: Ideal for electronics housing, covers, casings, battery holders, home automation devices, and more. Medical Devices: Suitable for covers and housings in various medical applications. Automotive: Excellent for use in electric vehicles, providing robust and reliable components. HP 3D HR PA 12 FR enabled by Evonik is set to revolutionize the way we approach manufacturing in multiple industries. Its unique combination of flame-retardant properties, high powder efficiency, and premium aesthetics makes it a standout choice for producing quality parts that meet stringent safety standards. [...]
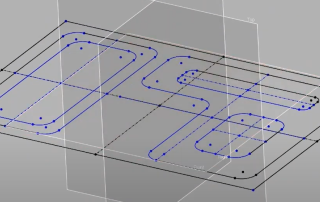
Modeling from a 2D Drawing with Design X Go
Modeling from a 2D Drawing with Design X Go Let’s explore some of the CAD modeling capabilities of Design X Go without the need for a scan, and how you can open the created model in Mastercam for toolpath generation. Unlocking CAD Modeling Potential When you have something like a 2D Print or a DXF file of a part, Design X Go enables you to transform these into a 3D model suitable for CNC programming using Mastercam’s dynamic tool pathing capabilities. Creating and Constraining Sketches Design X Go allows you to create base sketches, apply dimensional constraints, and use profile offsetting to form complex shapes. You can easily manage constraints to simplify your sketches and ensure accuracy. Utilizing Existing Geometry With tools like Convert Entities, you can leverage previously created geometry to build new sketch entities, streamlining the modeling process and ensuring consistency across your design. Modeling Complex Features Design X Go supports the creation of intricate features such as stepped pockets and filleted corners. By using a combination of lines, trimming, and dimensional constraints, you can accurately model detailed parts. Extruding and Finalizing the Model Once your sketches are complete, Design X Go provides robust extrusion capabilities to form the main base [...]
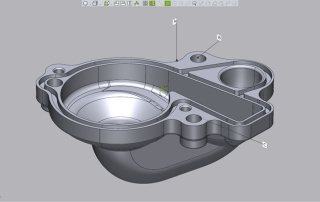
Batch Processing in Control X Professional
Batch Processing in Control X Professional This month, we continue to explore the Control X Professional Automation tools. Last month, we took a look at the Airfoil Analysis tool. This month, we focus on Batch Processing. Batch processing enables the user to create an inspection plan using a nominal CAD model and can then automatically assign the same inspection criteria to any number of scans, located on the user’s network. First, let’s explore each of the Model Manager tools used to inspect this water pump housing. Watch the Video Nominal CAD model First Scan to be Inspected The Datums used to align this and future scans to the same nominal CAD model A 3D Color Map, showing global tolerances that fall within an acceptable range Random deviations at point locations, showing critical areas of the housing Critical Hole Locations GD&T Specified on the Print 2D Fillet sizes Then once the inspection of the initial scan is completed, checked and tested, the identical inspection plan is then applied to any number of additional scans of manufactured parts using the Batch Processing tool. This [...]
Unlocking Growth with Flexible Monthly Payments Solutions
In the rapidly evolving 3D printing industry, financing is a strategic tool for businesses to stay competitive while managing cash flow efficiently. Flexible financing options allow companies to align payments with their operational and financial needs, such as matching payment schedules to revenue streams or internal budgetary cycles. This approach enables businesses to invest in cutting-edge technology with limited financial strain or disruption to day-to-day operations. Financing helps businesses preserve capital by reducing upfront costs and keeping monthly payments manageable. This preserves liquidity, ensuring funds are available for critical areas like R&D, marketing, or scaling production. By maintaining financial flexibility, companies can quickly seize new opportunities and adapt to changing demands, supporting long-term growth and stability. Leasing options further enhance flexibility, making it easy to upgrade or replace equipment as technology advances or market needs shift. Cimquest has partnered with PEAC Solutions to offer a range of tailored monthly payment plans. Together, we provide solutions that drive growth, keep your business competitive, and ensure you’re always ready for what’s next. These solutions are designed to help businesses to acquire the resources they need to grow while staying financially agile in today’s dynamic marketplace. Cimquest is proud to partner with PEAC Solutions and offer [...]