Additive Manufacturing of metals originated in the early 1990’s through a process known as direct metal laser sintering. This process uses laser toolpaths to weld powdered metals into three dimensional parts.
While effective, the technology has major barriers to entry due to the volatile nature of metal powders. These powders are reactive and can cause fires, requiring significant investments in infrastructure, including explosion proof rooms, respirators, and not to mention highly specialized operators. All of these requirements result in a high startup cost that can discourages widespread adoption of the technology.
With the Desktop Metal Studio Solution, many of these traditional obstacles are eliminated. The solution is the first office-friendly metal printer and it is similar to the safest, most widely used 3D printing process, FDM.
Let’s explore the process:
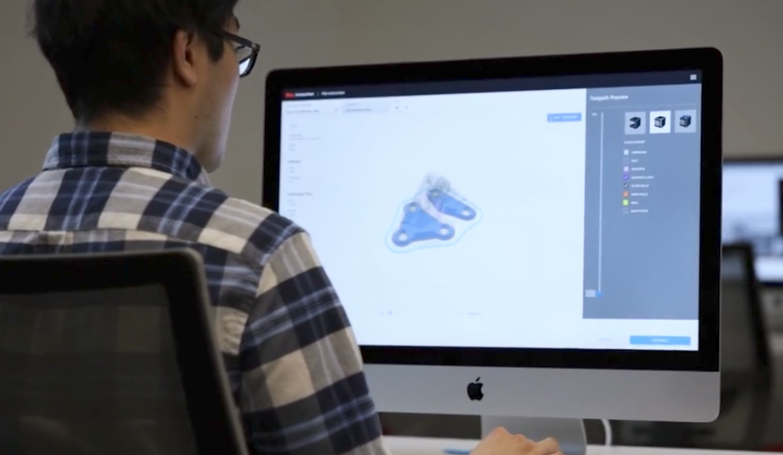
To begin, a digital model is prepared.
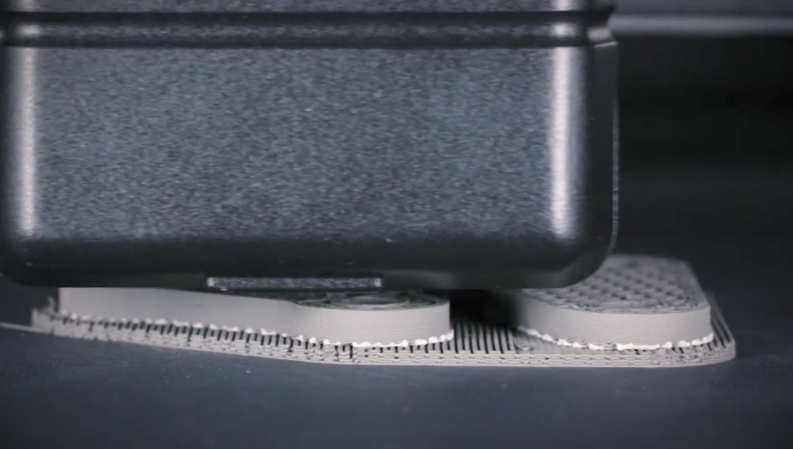
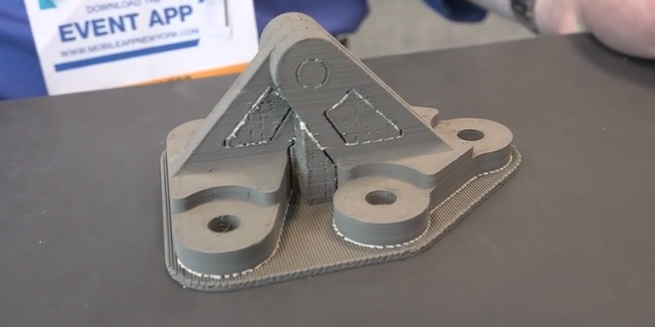
The file is sent to the machine and the printer extrudes rods that have metal powder bound within wax and plastic in a process called Bound Metal Deposition or BMD.
The resultant part is known as the “green part”.
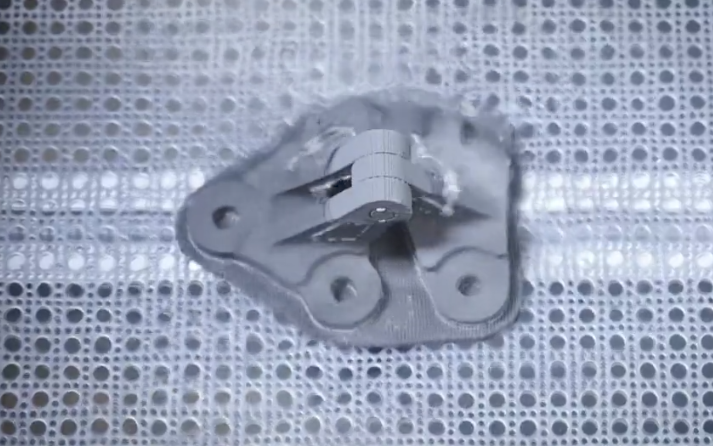
In the next phase, the part is submerged in a solution to remove wax from the bound material.
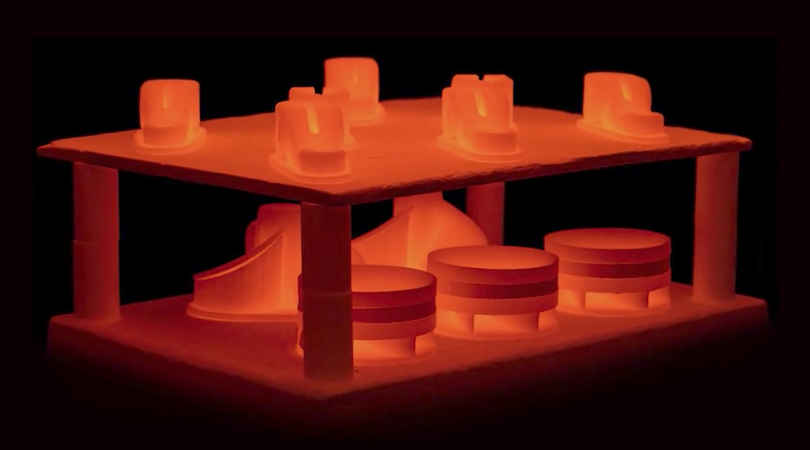
It is then placed in a microwave-enhanced furnace, which heats the part to temperatures near melting.
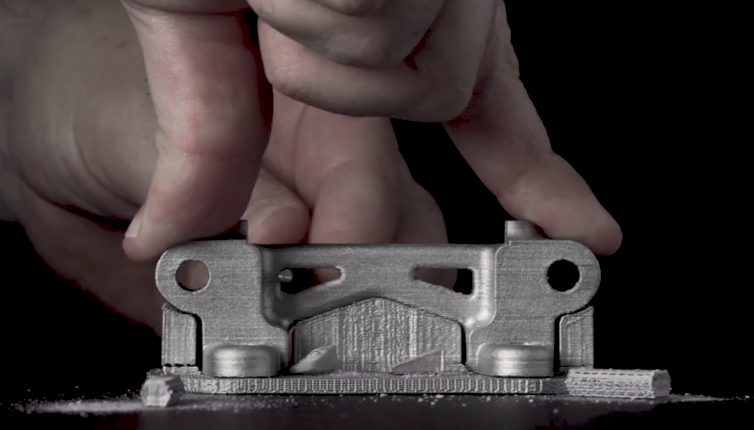
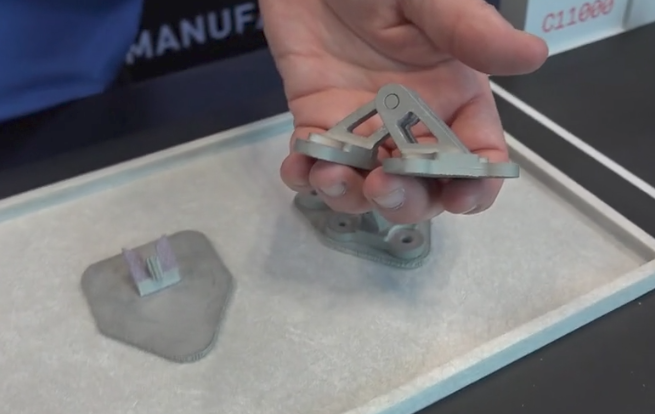
In this sintering phase, the part shrinks by roughly 20% and densifies to between 96 and 99.8%. Once removed, you have a finished part in which you can apply optional finishing such as machining or bead blasting.
While current metal 3d printing supports are removed with machining, the Desktop Metal Studio uses a proprietary ceramic release layer which can be removed by hand.
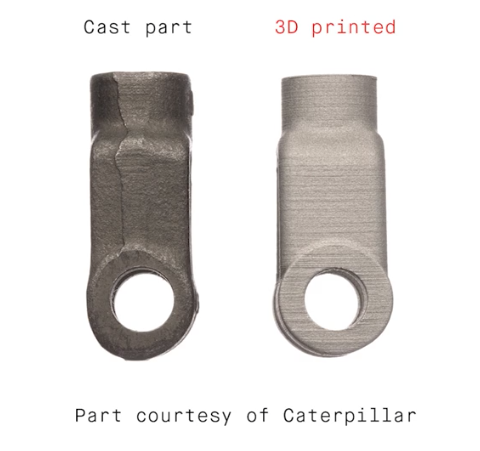
Final parts are near net shape and perform similar to wrought alloys.
Six materials will be available at launch, such as 316 L, Inconel 625 and Copper but the technology will have ultimately access to a wide range of metals from the MIM industry (over 200 materials compatible), including aluminum, super alloys, and titanium.
Cimquest will be taking delivery our first Desktop Metal Studio Printer in the very near future. At that point, we will begin testing and determining best practices. So look out for a Cimquest special edition with everything you will need to know about running a Desktop Metal machine.
The Desktop Metal Studio brings metal 3D printing into the office environment, making low cost prototyping of metal parts accessible, user-friendly and cost effective.
For more information on Desktop Metal printers, please click the button below.













Leave A Comment